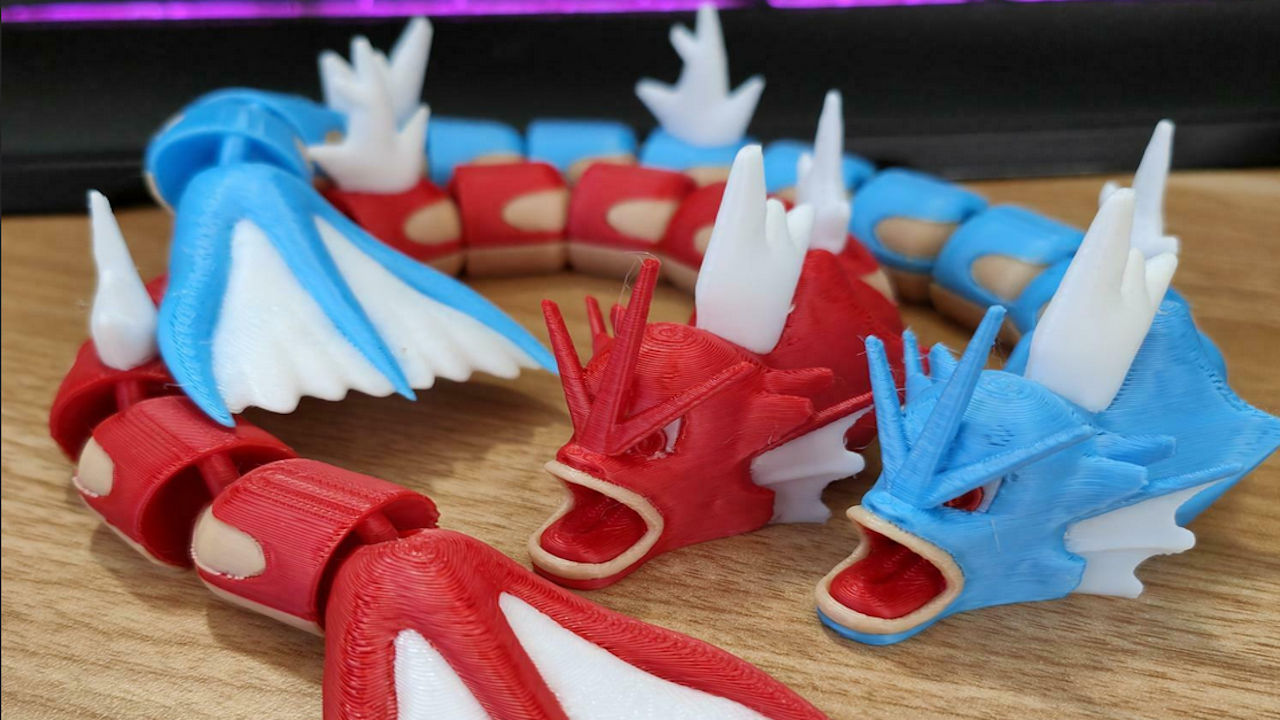
Everyone’s favorite flexible filament, TPU is stretchy, can take strong impacts, and looks great when 3D printed. TPU filament makes for fantastic looking flexible parts, and is a fun 3D printer filament for hobbyist projects as well as for rapid prototyping.
This article not only recommends the best TPU filaments for your projects as well as the best 3D printers for TPU, but also explains the advantages and disadvantages of TPU versus other filaments, as well as key best practices for fantastic looking TPU 3D prints.
- This article focuses on TPU. We also have another guide to every flexible filament.
- We also recommend the best TPU filament brands
TPU Filament 3D Printing Properties
TPU, or thermoplastic polyeruthane, is a plastic filament often used in FDM 3D printing to create flexible parts. It has a higher glass transition temperature than PLA (60-65C), at around 80C, and can handle low temperatures well without becoming brittle.
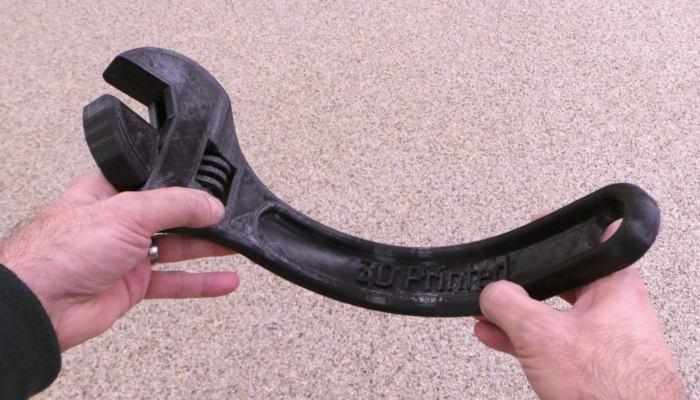
TPU is fairly strong despite being so flexible and stretchy, and can absorb considerable impact and general wear and tear without being too affected. It’s also slightly more rigid and easier to 3D print than other flexible filaments, leading to wider adoption than other flexible filaments.
Clear TPU filaments exist for those who want transparent, flexible prints, and a major positive is that TPU prints without any of the odors associated with ABS 3D printing. TPU 3D printed parts are however not food safe.
TPU melting point & print settings
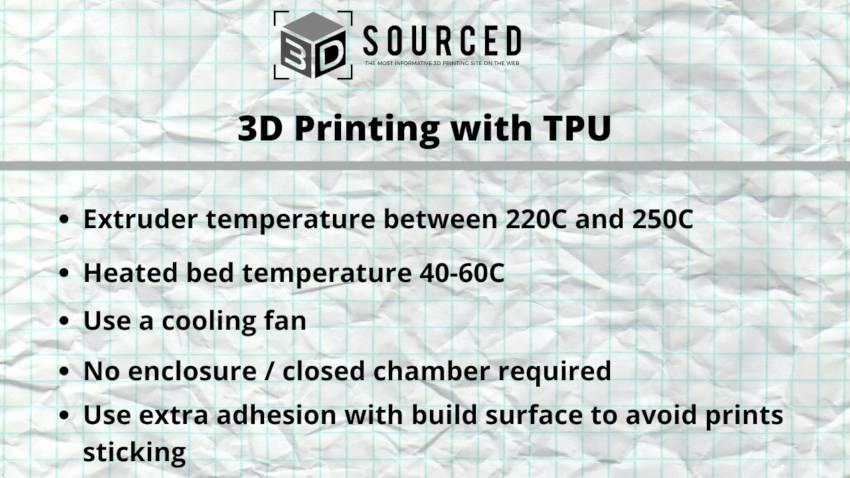
The general consensus is that the best 3D printing temperature for TPU is around 230C, with a wider range of between 220-250C.
Though you do not absolutely have to use a heated bed, it is highly recommended, at around 50C, though some go as low as 40C or as high as 60C.
It is recommended to use a cooling fan with TPU.
TPU 3D printing speed
We highly recommend reducing your print speed when 3D printing TPU. This can be frustrating, especially if you have invested in one of the fastest 3D printers around, but it will be far worse having to continuously unclog your 3D printer’s nozzle if you print too quickly.
We recommend printing at around 20-30mm/s with TPU. This is because TPU’s softness makes it more difficult to consistently extrude the right amount of filament, which can cause clogging, errors, and failed prints. It is better overall to go slow and steady, rather than go hell for leather and have to keep unclogging.
These settings should be slower across the board. Print your first layer, supports, perimeters and have retraction speed slowed down for more reliable TPU 3D printing.
With a Flexion extruder you may be able to print slightly faster, at around 30-40mm/s. Flexion extruders are specifically designed for flexible filament 3D printing, and can handle the nuances and coiling of filaments like TPU better.

TPU Build Surface
Use a build surface like PEI or blue builder’s tape along with glue stick or similar for adhesion. Be careful however if you are using PEI sheets, as TPU sticks very well to these sheets. Use extra glue stick or other surface for adhesion to prevent parts pulling off the PEI sheet after printing and fusing with it.
Bowden vs direct drive extruder for TPU
Direct drive extruders are considered better than bowden extruders for TPU, though Bowden extruders can work fine with the right settings. This is because direct extruders are directly connected to the hot end, and therefore there is less travel distance between the extruder for filament to clog, coil or cause any other kind of error.
With a Bowden extruder, flexible filaments have a longer travel distance to the hot end, and can cause problems if the TPU filament coils and clogs along the way. For this reason, makers using a 3D printer with a Bowden extruder may want to consider reducing print speed even further, down to around 15-25mm/s.
How much does TPU filament cost?
TPU is slightly more expensive than ABS and PLA, starting at around $35 for starting blends on sites like Amazon. Higher quality TPU filament starts at around $45-$50, and is available on Matterhackers.
Best TPU Filament
Options include:
- Hatchbox TPU filament on Amazon for $35
- MH Build Series TPU on Matterhackers for $45
- NinjaTek NinjaFlex TPU on Matterhackers for $55 (0.5kg)
- 3DJake UK & Europe TPU selection
For a full guide, read our best TPU article.
Advantages of TPU Filament
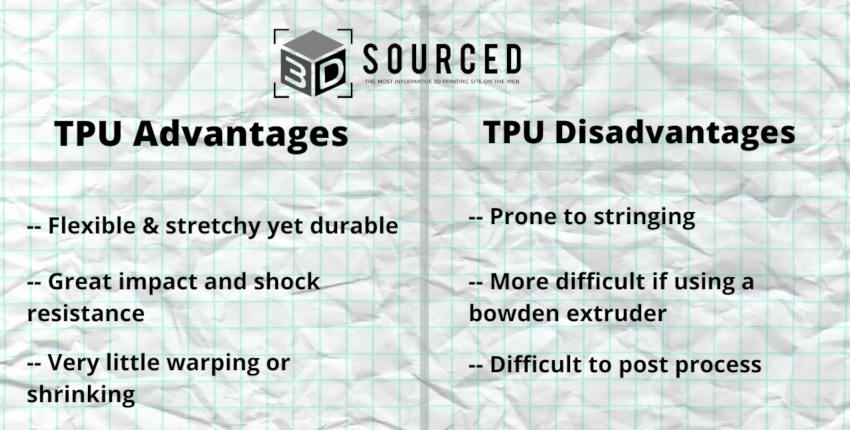
- Flexible and soft: TPU is the most widely used flexible filament for elastic parts, able to create stretchy parts with ease.
- Excellent impact resistance and vibration dampening: the flexible nature of TPU filament makes it a fantastic material for taking strong impacts and mitigating vibrations.
- Best for bendable prototypes: prototypes that need to be tested and bend are perfect for TPU 3D printing. TPU prints easier than other flexibles, can handle a range of temperatures, and is chemically and abrasion resistant, making it perfect for functional flexible prototype testing.
- Available in many colors: like PLA or ABS, TPU comes in a range of colors, from standard black, grey and red to clear transparent filaments.
- Very little warping: this makes it great for long and thin parts that would otherwise curl if printed in ABS.
TPU 3D Printers
Some cheap 3D printers can print TPU without much issue, though a number of these more basic printers struggle. We have included a list below of some of the best 3D printers in each price range that are known to be able to handle TPU.
| Name & Brand | Build volume (mm) | Price | Best price available at: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creality Ender 3 | 220 x 220 x 250 | $215 | Amazon here |
| Creality Ender 5 Pro | 220 x 220 x 300 | $400 | Amazon here |
| Flashforge Creator Pro | 227 x 148 x 150 | $600 | Amazon here |
| Pulse XE | 250 x 220 x 215 | $999 | Matterhackers here |
Disadvantages of TPU filament
- Often strings: TPU filament is prone to stringing, which although can be removed afterwards fairly easily, is still a hassle. Optimize print settings to prevent this.
- Worse for Bowden extruders: extra care must be taken if printing with a Bowden extruder, as filament is prone to clogging and coiling, especially during the longer travel distances to the hot end.
- Difficult to post process: TPU is known for being difficult sand and improve the surface finish of. However, recent experiments of heating TPU parts up for short amounts of time at high temperatures in ovens have created glossier finishes, but be extremely careful. 3DMN has a great video showing this process on YouTube, you can view the video here.

Optimize the following settings for the best TPU 3D printing results:
- Use a direct drive extruder: direct extruders minimize the distance to the hot end and nozzle. A shorter travel distance means there is less opportunity for filament to coil or jam.
- Slow feed rates: at higher speeds TPU filament can compress and jam, so it is always best to be slow and steady. TPU’s elasticity makes it hard to control under sudden changes in print speed, and will be frustrating to keep unclogging. 20mm/s may feel slow, but it’s consistent.
- Mount spool so filament is pulled downwards: mounting your TPU filament spool above your 3D printer means filament is pulled downwards, rather than upwards. This is more important as TPU’s flexibility can cause errors.
- Use the correct 3D slicer settings: For example, reduce stringing in your 3D slicer by setting your printer to avoid traveling through open spaces on the print. Simplify3D can do this, as can Cura.
TPU Applications
TPU is often used in the manufacturing of phone and tablet cases. Its ability to absorb shocks, vibrations and impacts also makes it great for tires, as well as many other custom rubber parts used as shock absorbers.
TPU is also used in 3D printed shoes, especially in shoe soles. Several interesting 3D printed shoe projects have used TPU filaments, as well as PEEK. Additionally, TPU is sometimes used for caster wheels and those seen on chairs, desks, and other appliances like drive belts.
How to Store TPU
TPU is hygroscopic, meaning that it absorbs small amounts of moisture from the air. Without airtight storage TPU filament will begin to deteriorate significantly over the course of just a few days. Specialized filament storage containers can remedy this, which we recommend below.
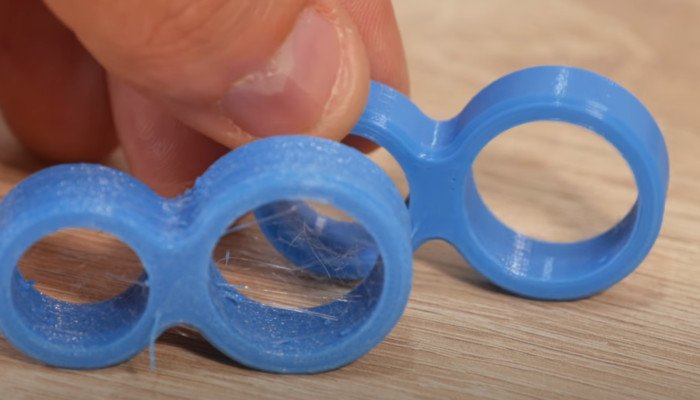

Without good storage and desiccants, prints with TPU come out noticeably rougher, with an uneven surface finish, a holey appearance and more stringing. Filament dryers, such as one we recommend below, can restore the smooth surface area TPU filament is capable of, by removing most of the accumulated moisture.
We recommend the following:
- Printdry Filament Storage Containers — for storing filament and preventing moisture from ruining TPU qualities
- Printdry Filament Drying System — for drying filament to improve surface finish
Some people recommend putting TPU filament that has been out in the open into an oven for 30 mins to an hour at around 70C to heat off the moisture that can ruin the filament. 3DMN has shown the difference on his YouTube channel when you heat TPU like this.
Other articles: