Key Takeaways
- Extruder: The part that feeds and melts the filament, and deposits it through the nozzle. It consists of a cold end and a hot end.
- Print bed: The surface where the print is formed. It can be heated or unheated, and has different materials and coatings for adhesion and removal.
- Motion system: The parts that control the movement of the extruder or the print bed along the X, Y, and Z axes. It includes stepper motors, belts, rods, end stops, and drivers.
- Controller board: The computer that translates 3D models into print instructions and regulates the printer’s temperature, speed, and accuracy.
3D printers, with their various parts and intricacies, may seem intimidating at first. But trust me, it’s far simpler than it looks.
This guide will demystify your 3D printer by explaining each part with brief description of each component, along with a summary of its function.
I’ll also share my tips on how to get peak performance from each part from over 5 years of 3D printing experience.
While the majority of this guide pertains to standard FDM 3D printers, I’ll also touched upon the unique aspects of delta and resin 3D printers to cover the key differences.
Jump to Each 3D Printer Component Here
3D Printer Parts Section 1: Parts Directly Involved in Printing Process
Extruder
The 3D printer extruder is the central hub of the printing process, and covers both the cold end and the hot end.
The extruder’s cold end channels filament to the hot end, ensuring a smooth transition from solid to melted filament onto the print surface.
The hot end of a 3D printer is where the filament melts before deposition through the nozzle.
Recommended Extruder Parts:
| Name | Price | Best place to buy: |
|---|---|---|
| E3D V6 | $61 | Amazon here |
| E3D Lite6 | $37 | Amazon here |
| Micro Swiss MK10 All Metal Hot End | $63 | Amazon here |
| Diabase Flexion Single Extruder | $150 | Amazon here |
| Diabase Flexion Dual Extruder | $250 | Amazon here |
| E3D Titan Aero | $140 | Amazon here |
Cold End Components
Filament drive gear: Also known as a hobbed gear, this part grips and propels filament towards the hot end. Its quality is crucial to prevent clogs and errors.
Idler gear: This wheel, similar in appearance to the drive gear, maintains filament tension against the drive gear. Adjustable in most printers, it helps prevent clogs by securing the filament during its journey through the cold end.
Feeder system: Comprised of either a Bowden or Direct Drive Extruders:
- Bowden feeder system: These systems separate the cold and hot ends, reducing the mass at the print head for faster printing. Typically, a PTFE tube guides filament from the cold end to the hot end. Bowden extruders are standard in delta 3D printers.
- Direct feeder system: These systems place the cold end directly above the hot end, reducing the filament’s journey, which is particularly useful for flexible filaments. The shorter travel distance also reduces the chance of blockages.
- Dual extruders: Some 3D printers feature two extruders, enabling dual-color printing or support printing with soluble filament materials like PLA. A independent dual extruder system, such as those offered by BCN3D, even allows for simultaneous printing of two different objects.

Hot End Components
Depending on your printing material, you may require a durable metal hot end instead of a standard PEEK one.
While PEEK hot ends can handle up to 230C—suitable for ABS and PLA—they struggle with more resilient materials like PETG and Nylon.
Metal hot ends, on the other hand, can withstand higher temperatures, offer reliability, produce less ooze, yield crisper prints, and are typically easier to clean.

Parts of the hot end include:
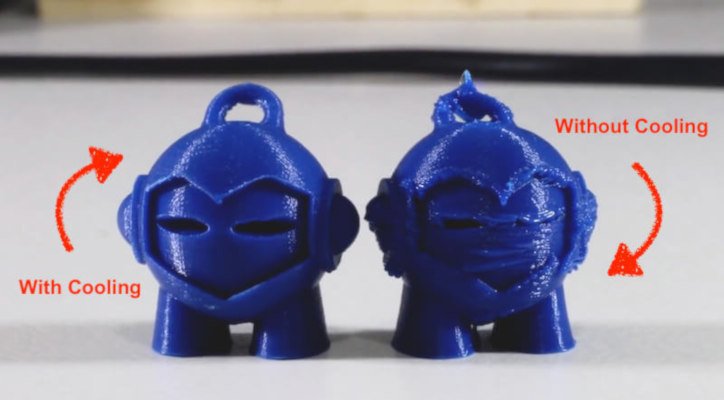
- Heat sink: Prevents premature filament melting before it reaches the nozzle, a common cause of jams, especially with PLA filament.
- Heat sink fan: Rapidly cools deposited filament, helping it retain shape and avoid deformities. This is particularly useful for delicate overhangs, bridge structures, and producing sharper edges. Without a fan, gravity can distort the molten plastic before it solidifies, leading to a misshapen printed object.
- Heater block and cartridge: These parts heat and melt the filament.
- Thermistor: This sensor monitors the heater block temperature.
- Nozzle: We delve into nozzles in more detail in the next section.
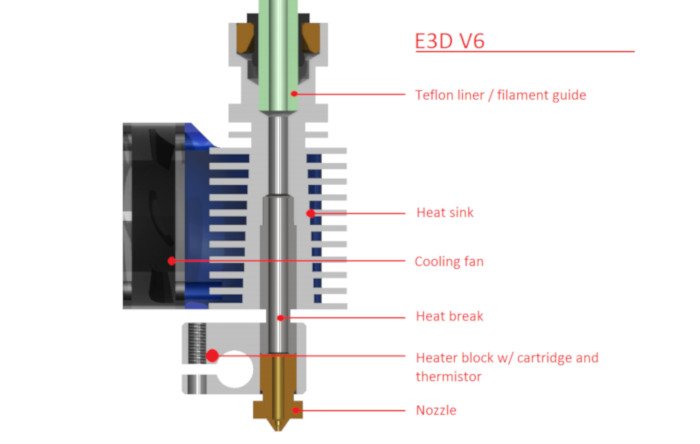
Nozzle
The 3D printer nozzle, attached to the hot end, is where filament extrudes onto the print bed surface to create the model. Your choice of nozzle impacts print quality, as its size can significantly impact your ability to extrude different filament materials and diameters smoothly.
Some Nozzles I Recommend:
| 3D printer nozzle material | Where to buy | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Brass | Amazon here | $9 (for 24 nozzles) |
| Stainless Steel | Amazon here | $7 (for 5 nozzles) |
| Hardened Steel (by E3D) | Amazon here | $19 |
| Ruby-tipped (by Olsson Ruby) | Amazon here | $93 |
Nozzles ranging between 0.15mm and 0.4mm offer high precision, enhancing the accuracy of fine details in your prints. However, larger nozzles provide a speedier and more reliable printing process less prone to clogging.

Nozzle durability varies with the material used in its construction. Standard brass nozzles are compatible with most filaments, but their frequent replacement may be necessary due to rapid wear. In contrast, stainless steel nozzles and hardened steel ones offer enhanced longevity.
Print Bed
The print bed, where the filament becomes the final part, is typically heated, enabling use of robust filaments like ABS, PETG, and PC. Unheated versions, found on affordable 3D printers like Dremel 3D20, are restricted to PLA and TPU.
A heated printing bed helps to mitigate warping issues by slowing the cooling rate of the plastic. Materials for these heated print beds range from glass to aluminium, with the former being more prevalent due to its ease of maintenance and flatness. Many print beds offer flexibility, simplifying print removal.
The print bed surface aids print adhesion and eases removal. The first layer of a print is laid here, setting the stage for subsequent layers. An irregular first layer affects subsequent ones, compromising print precision.
Different materials work best on specific surfaces – you can check our full build plate guide to learn more.
If the print bed is incorrectly positioned, print quality will suffer. Increasingly, 3D printer print beds can auto-level, but some still require manual adjustments via bed screws.
Cartesian printer beds are either square or rectangular, while Delta printers have circular printer beds.
3D Printer Parts Section 2: Parts Involved in the Backend
Motion Systems
Stepper Drivers: Commonly a NEMA17 (though NEMA14, NEMA23, and NEMA24 are prevalent), stepper drivers propel the extruder in precise steps, executing mechanical movements as instructed by the controller board.
Belts: These facilitate the extruder’s accurate movement on the X- and Y-axes, impacting the printer’s precision and speed. In Delta printers, they control the Z-axis. Correct belt tension is crucial to maintain print quality.
Threaded Rods/Leadscrew: Threaded rods, connected to the stepper motors, manage the Z-axis, allowing the print head to move up or down. In some cases, they move the print bed. Leadscrews, a pricier alternative, offer smoother movement.
End Stops: These sensors enable the printer to detect its position along each axis, indicating when an axis end has been reached.

Controller Board
Often referred to as the mainboard or motherboard, the controller board is the central computer of the 3D printer, issuing precise instructions to the printer’s mechanical components based on the STL file coordinates.
The board’s quality directly influences print precision. Even with accurate hardware, incorrect movement instructions result in imperfect prints. A superior mainboard dispatches pinpoint commands, ensuring clear and precise part formation.
The controller board does more than directing motion. It translates 3D models into print coordinates and regulates the printer’s temperature. Thus, while the extruder physically forms the filament, the controller board serves as both the heart and brain of the 3D printer.

Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The PSU supplies power to the printer for filament melting and the printing process. More powerful PSUs enable the use of higher temperatures filaments like ABS, PETG, and Nylon, while less powerful ones often limit you to PLA.
Remember to choose a 3D printer and power supply unit compatible with your country’s voltage standards.

3D Printers Parts Section 3: Parts Involved in Structure
Frame
3D printer frames play a crucial role in ensuring part quality by providing stability and preventing disruptive vibrations.
Contemporary 3D printers usually use metal frames, but some still use acrylic. Early FDM 3D printer kits, including the initial Ultimaker models, featured wooden frames. Notably, some DIY kits use plastic frames printed by other 3D printers, particularly within the RepRap community.
A sturdy, weighty frame is key to high-quality prints with smooth surface finishes. Many models feature enclosed framesthat help maintain a consistent printing temperature particularly and protect from dust.

Interface
Typically equipped with a touchscreen LCD, some 3D printers like the Creality CR-10 feature a rotating knob for navigation. These interfaces allow easy access to the printer’s various features and settings, including calibration on certain models. An enhanced user interface can provide additional print statistics, such as estimated time remaining.
While plenty of 3D printers offer WiFi connectivity for remote printing, most desktop models still rely on a USB port or SD card.
Filament
3D printer filaments are the materials melted and extruded to create parts on FDM 3D printers. These filaments are wound on spools, then guided through the extruder to the hot end, where they’re melted and accurately deposited through the nozzle.
While most modern 3D printers utilize 1.75mm filament, some are designed for larger sizes.
Different filaments melt at different temperatures, and most filaments require a heated print bed for an effective printing process. PETG and Nylon filament require metal hot ends due to their higher melting temperatures, which are beyond the capacity of PEEK hot ends.

Part 4: Extra Delta 3D Printer Parts
Delta 3D printers use effectors rather than stepper motors for motion control. These effectors control the three arms that move the extruder into the correct place during the printing process. These three arms meet in the center and conect to the extruder, allowing them to move the extruder in any direction across the three axes to deposit filament.
3D Printers Parts Section 5: Resin 3D Printer Parts
The main parts of a resin 3D printer vary based on the type (LCD vs SLA vs DLP), but include:
- Resin vat: also known as a resin tank, contains the resin to be cured
- Light source: either an LCD, DLP projector or SLA UV light source
- Build platform: where the printed object is formed, and moves up or down when each layer is finished
- Resin: variety of types, such as daylight-sensitive, castable, UV resins
- Roller: some models feature a roller that glides over the built platform, ensuring the resin is adequately set.




