The lowest-cost 3D scanners start at around $150, though these are often DIY kits which require assembling or sometimes 3D printing some parts. Higher-quality handheld 3D scanners cost between $2,000 to $5,000, while professional 3D scanners for reverse engineering, professional design, and demanding 3D visualizations can cost up to $30,000.

There’s a huge difference in pricing between 3D scanners, which is affected by factors including:
- Size and complexity of the object you want to scan
- The scanner type and technology
- 3D scan quality (accuracy, resolution)
- Time the project takes (for renting a 3D scanner)
- The ability to 3D scan in color
- Shipping costs
- Software and post-processing
Fortunately, there are scanners for all budgets and applications, and we’ll explain in more detail what specs and uses you can expect in each price range.
Here’s How Much Each Type of 3D Scanner Costs
To better understand the cost associated with 3D scanners, we’re diving into the different types of 3D scanners you can buy.
| Type of 3D Scanner | Price | Popular 3D Scanners in this Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | Under $2,000 | CR-Scan Ferret, Revopoint POP 3, Revopoint MINI, Shining3D Einstar |
| Mid-Range Handheld | $2,000 to $30,000 | Shining 3D Einscan Pro HD, Creaform HandySCAN Silver 307, Artec Micro 2 |
| Industrial | $10,000+ | Artec Eva, Creaform HandySCAN Silver 307, eviXscan Optima+ M, ScanTech SIMSCAN, Zeiss Gom Scan 1 |
Entry-Level 3D Scanners: Under $1,000

3D scanners priced under $1,000 are considered entry-level and are aimed at hobbyists and small businesses with modest needs.
Though we have a dedicated guide to the best cheap 3D scanners, here are some of the top-rated scanners in this price range:
| Scanner | Price | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CR-Scan Ferret | $320 | Budget scanner that offers great value for the price and is ideal for 3D printing |
| Revopoint POP 3 | $659 | General purpose scanner suitable for medium to large objects |
| Revopoint MINI | $799 | Designed to capture small, detailed objects such as jewelry |
| Shining3D Einstar | $959 | Great option for small businesses that want more quality and versatility over lower-cost alternatives |
These low-cost scanners work well for applications like 3D printing, basic digital archiving, product modeling for e-commerce, basic design work, and simple AR/VR. They rarely capture with accuracy below 0.1 mm, limiting the detail level they can reproduce in scan results. This limits their applications beyond hobbyist fun projects.
They are by no means geared to professional or industrial applications like reverse engineering, that demand uncompromising dimensional accuracy and scan quality.
For the lower price, you also sacrifice usability. While professional-grade scanners allow you to scan an entire object with a single press of a button, scanning with low-cost models is time-consuming, and scan times tend to be much longer due to slower capture speeds, which rarely go higher than 30 FPS.
That said, for under $1,000, you can still expect features like full-color scanning, robust post-processing software, handheld/static scan modes, anti-shake technology to improve scan quality, and Wi-Fi 6 connectivity to speed up data transfer speeds after scanning an object.
We cover a number of scanners in this price range in our top 3D scanners buying guide.
You can even use your phone as a 3D scanner. Even more basic Android models and older iPhones can use photogrammetry 3D scanning apps to create 3D models, and the newer iPhones have LiDAR sensors for better quality 3D scanning. However, these are still not as high quality as specialist 3D laser scanners.
Handheld 3D Scanners: $2,000 to $30,000

Handheld 3D scanners are designed for portability and mobility – without sacrificing quality. Prices for professional handheld 3D scanners range anywhere from $2,000 to $30,000. Many jewelry scanners also fall into this category.
Typically, handheld and professional 3D scanners are used for reverse engineering, conservation work, digital archiving, jewelry design and repair, floor plans, interior design, and product design in the automotive and aerospace fields.
Professional scanners offer much better accuracy than lower-cost options. Expect around 0.5 mm as standard, dropping as low as 0.04 mm for the pricier options. With this level of detail, you can capture the intricacies of both large and small objects, such as engine parts, intricate jewelry, and subtle facial details. They also excel in use cases like inspection and quality control.
Here’s a selection of the most popular handheld 3D scanners on the market:
| Scanner | Price | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Shining 3D Einscan Pro HD | $5,000 | Multi-purpose handheld scanner ideal for reflective or dark surfaces |
| Creaform HandySCAN Silver 307 | $20,000 | One of the best jewelry scanners out there with a 5-micron accuracy |
| Artec Micro 2 | $25,000 | One of the best jewelry scanners out there with a 5 micron accuracy |
Industrial 3D Scanners: $10,000+

Industrial 3D scanners are top-of-the-range scanners that cost upwards of $10,000.
Due to their price, industrial scanners are typically reserved for larger businesses specializing in specific fields where extreme accuracies and tight tolerances are essential. These include:
- Reverse engineering
- Product design
- Architecture
- Rapid prototyping
- CGI, and AR/VR
- Scientific measurements
- Automobile and aerospace applications
These commercial 3D scanners have the highest accuracy, resolution, and resolution. Expect an accuracy below as low as (or even lower than) 0.009 mm, which will bring out the smallest surface details with almost flawless dimensional accuracy.
Many also offer larger maximum scan volumes for car, human body, and room scanning. Most also come with commercial software that improves workflow and makes scanning easy, while offering various advanced options to refine and export 3D models.
Here’s a selection of the most popular industrial 3D scanners on the market today:
| Scanner | Price | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Artec Eva | $17,000 | Suited to medium-sized objects in fields such as health care, orthopedics, archaeology, and prosthetics |
| Creaform HandySCAN Silver 307 | $27,900 | Designed for scanning small to medium objects with complex surfaces and details |
| eviXscan Optima+ M | $30,000 | Offers an incredible level of details optimized for quality control and rapid prototyping in demanding industries |
| ScanTech SIMSCAN | $30,000 | A palm-sized handheld scanner designed for narrow and hard-to-reach places in engines, buildings, and vehicles for quality control and inspection work |
| Zeiss Gom Scan 1 | $27,000 | Offers an incredible level of detail optimized for quality control and rapid prototyping in demanding industries |
3D Scanning Service Costs – To Rent
3D scanner services cost anywhere from around $200 for a simple scan of a small object, up to more than $2,000 for large, complex objects. Per-hour costs fall roughly around $150-200/hour in the majority of cases.
However, these are ballpark figures and prices can vary greatly depending on several factors. For this reason, most 3D scanning services will offer you a specific price based on the project, rather than set pricing.
Here are the factors that affect the cost of 3D scanning:

1. Size and complexity of the object
Larger objects typically take longer to scan than smaller ones, which costs more. 3D scans are made using individually captured frames that are then stitched together to create a finished model. Larger objects involve more frames and time to capture.
However, the complexity of the object also affects the price. For example, an ornate heirloom ring with intricate details, edges, gaps, and a reflective surface will take longer to scan (around 20-30 minutes) than a large object with flat, featureless surfaces like a hammer or wrench (5-10 minutes).
It’s not just the scanning time that affects cost, either. It will also take longer to process and post-process the ring 3D model, which adds to the cost.
2. Time the project takes
Because 3D scanning services typically work on an hourly basis, projects that require more hours to complete will cost more than fast scans.
For example, if you’re scanning an entire house for a real estate listing, expect to pay upwards of $3,000, while if you want to scan a single part, for example a radiator grill, budget for between $500 to $800.
3. Color scanning
A full-color scan with texture and surface details typically adds to the overall price. Color is generally needed for applications like digital media, e-commerce, VR/AR, and game design.
The extra cost comes from the extra time needed to set up suitable lighting for the scanning process and the more demanding post-processing of scan data.
4. Shipping costs
It’s important to factor in the cost of sending an object to the service if you cannot deliver it in person.
Larger objects incur higher shipping fees, as do multi-object projects. For example, shipping a 50lb object in an extra large box with Fedex from New York to Boston costs around $200.

5. Software, post-processing, and additional services
Though some services will give customers the raw scan data, most factor software and post-processing into their costs to finish the 3D model.
Many also offer additional services such as CAD modeling, color texturing, and texture mapping, which add to the cost. Expect to pay an additional $100-$200 for these, though the complexity and size of the part factor here as well.
6. Scanner type, quality, and resolution
The better quality and more expensive the scanner costs, the more expensive the service will be. Pricier scanners offer better dimensional accuracy and precision, so you get what you pay for.
A hobbyist using a budget scanner like the CR-Scan Ferret may charge $15 per object, while an established service running a Artec Micro II may charge $300 for the same scan.
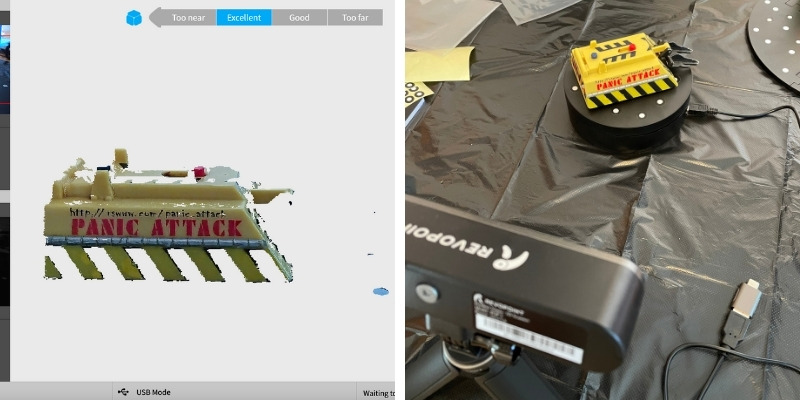
7. Service fees
3D scanning costs are also affected by what we’ll call “service fees,” which include:
- Manual labor costs
- The expertise of the operator and the cost put into their training
- Maintenance and running costs, such as repairs, utility costs, unforeseen issues, and the depreciation of the 3D scanner
Should You Buy Or Rent a 3D Scanner?
Given the cost of hiring a 3D scanning service, there is a point where it becomes more cost-effective to buy one outright. You need to evaluate how often you need to use the 3D scanner, and how complex the objects are, to gauge whether it’s better value to rent or buy.
For example, if you were to scan two fairly large and complex car parts a week at $800 each, this would cost $1,600 per week, or $6,400 a month.
If you were to buy an industrial-grade scanner like the Einscan Pro HD for $5,000, you’d recoup the cost in less than a month. If you opted for a more precise model like the Artec Eva for $16,000, you would pay off the cost in less than three months.
Of course, this requires the skill to operate the 3D scanner (or training costs to gain this expertise). It’s hard to pin an exact number on these, but setting aside $500 a month for repairs is sensible. The scanner will also depreciate and lose value over time, but overall, for heavy users even with these costs factored in, buying a 3D scanner is cheaper than renting.
If you need to scan lots of objects within a short period of time, and then have months where you don’t need to scan at all, renting a 3D scanner is better. For example, Artec offers a rental service, which costs roughly $300 a day for the Artec Eva.
If you’re looking to buy a 3D scanner, I recommend reading our reviews and recommendations. We’ve broken these down into different categories: