For all their benefits to designers, architects, and engineers, CAD programs don’t come cheap, and when they do, expect to navigate a sea of commercial limits, sketchy data ownership rules, and reduced functionality.
Enter open-source CAD software, a boon for those looking for full ownership of their work, expandability, and unhindered customization.
We’ve pulled together a list of our top open-source CAD software recommendations in this guide. You’ll also find a few choice tips to find the right option to meet any potential needs and requirements.
Best Open-Source CAD Software
1. FreeCAD

FreeCAD is an open-source parametric CAD program designed from the ground up to cater to the most demanding applications in mechanical engineering, architecture, and product design.
You can download and use FreeCAD for commercial projects for free.
FreeCAD rivals paid heavy-hitters like AutoCAD and Fusion 360 for features and functionality. These include a fully decked-out 3D modeler alongside an integrated 2D drafting tool.
Advanced features include Boolean operations to easily modify intricate models, BRep objects to meld solid and non-solid geometries, NURBS surface and curves to create complex shapes and models, and a top-layer Python API to code bespoke tools, commands, and macros.
FreeCAD boasts a workbench system, each one a module for specific applications such as architectural modeling, CAM, CNC work, industrial robot simulations, technical drawing, rendering, and more.
With compatibility for Windows, Mac, and Linux, FreeCAD is also customizable, extendable, and supports open file formats like STL, DXF, OBJ, SVG, STEP, etc.
FreeCAD’s initial complexity is quickly demystified thanks to an archive of well-drafted documentation, catering to everyone from beginners to seasoned designers.
2. Blender
When a free, open-source CAD program is used for AAA games and visual effects in blockbuster films, you know it means business.
That’s precisely what Blender does and so much more.
Blender knits together a dazzling selection of features, including tools for 3D modeling, 2D sketching, sculpting, simulation, rigging, camera tracking, video editing, rendering, visual effects, and more.
These are, however, more geared towards creative applications, so Blender isn’t the best option for technical and mechanical projects.
On the community side, Blender development is user-led, centered around add-ons for virtually every application you could need.
Additionally, active contributors produce quality tutorials and documentation to accompany the program if you have questions or need guidance on any aspect of the toolset.
A steep learning curve and a daunting range of features stand as the only concerns about recommending Blender to anyone.
Despite being open-source and freely available for commercial projects, it is a professional tool that requires a considerable time investment to tame.
3. Art of Illusion
Art of Illusion offers a wealth of 3D modeling and rendering tools for animation applications, lining it up alongside Blender as an artistic-leaning option.
If you can look past the somewhat outdated interface, many of Art of Illusions’ features match those of paid CAD programs, with procedural textures, skeleton animation, a Boolean modeling tool, and surface modeling, to cite a few.
There’s also built-in scripting to allow users to extend and tweak the program.
The community helms Art of Illusion’s development, positioning it as a genuinely open-source project and granting free for-profit use to all.
There’s also substantial documentation and various tutorials to guide you through any potential issues. It’s compatible with Windows, Linux, and Mac, with the most recent update dated early 2021.
4. LibreCAD

LibreCAD differs from our other recommendations in that it’s an open-source 2D CAD program rather than software designed for 3D modeling.
LibreCAD is available free for Windows, Linux, and Max, with no limits on commercial use.
Delivering high-quality technical and mechanical 2D drafting and drawing, LibreCAD lends itself well to engineering, architecture, laser cutting, and CNC milling.
Standout features include a rich portfolio of shapes, dimensional tools, snap tools, hatching patterns, and multi-layer drafting capabilities. Thanks to the integrated CAM tools, you can also prepare projects for machining in a selection of the most popular file formats.
We also like LibreCAD for housing an intuitive and clean interface, somewhat reminiscent of AutoCAD.
It’s easy to learn, partly thanks to a vibrant community pumping out documentation and in-depth guides, and ready to help if you encounter any obstacles.
Furthermore, LibreCAD is designed to promote user modification and extensions. New features and updates pop up regularly, further extending LibreCAD’s already impressive toolset.
5. OpenSCAD
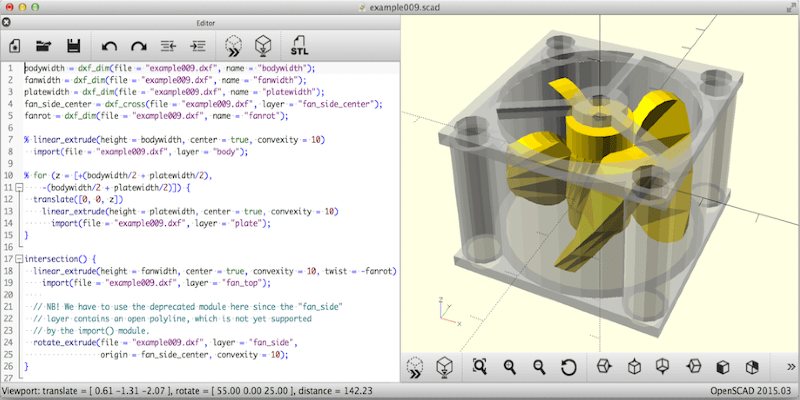
OpenSCAD is best described as a 3D compiler that creates solid 3D CAD models based on script files.
The user generates a script that defines the design parameters and renders the 3D model. The script determines every step, meaning users have complete control over the process and can easily modify any aspect of the model.
OpenSCAD offers both constructive 3D solid geometry modeling alongside 2D outlines, the latter importable from AutoCAD DXF files.
3D models can be exported in popular STL and OFF formats.
The script-based functionality makes OpenSCAD one of the most challenging open-source CAD software to master, so it isn’t recommended for anyone other than seasoned designers and coders.
With such a focus on coding, OpenSCAD best serves technical and mechanical modeling, making it a solid option for high-precision engineering and design applications.
You can download and use OpenSCAD for free. There are no commercial limits, and the program is compatible with Windows, Mac, and Linux.
6. BRL-CAD
BRL-CAD is a constructive solid geometry modeling CAD program with over 30 years of development under the hood.
BRL-CAD is chiefly used for engineering and creative graphical applications. The U.S. military even uses it for combat vehicle systems analysis and simulation.
BRL-CAD offers a comprehensive geometric editor, geometric analysis, system performance benchmarking tools, simulation tools, rendering with ray-tracing support, and powerful integrated scripting.
The program also ships with geometry libraries with different customizable modeling tools.
BRL-CAD is entirely open-source, meaning free use and customizable code. Compatibility extends to Windows, Mac, Linux, Solaris, and BSD.
BRL-CAD has a substantial learning curve, and the interface isn’t quite as user-friendly as our other recommendations, but few of these offer similar analysis and simulation tools.
7. QCAD

QCAD is open-source CAD software that, similar to LibreCAD, exclusively offers 2D drawing and sketching tools.
It regroups over 60 construction and modification tools and nearly three dozen CAD fonts. There’s also a stacked part library, boasting nearly 5,000 CAD parts.
QCAD is a solid option for quick sketching, mechanical drawings, mechanical parts, schematics, building plans, floor plans, and interior design planning.
A clean, simple layout and interface make it accessible to beginners all the way to experienced designers.
It’s available for Windows, Mac, and Linux. QCAD is available either as a free trial (limited to 15 mins sessions) or on a free, open-source license known as the QCAD Community Edition, a more-or-less full version minus a few advanced features.
Should you need CAM tools, there’s a paid QCAD/CAM version that offers toolpath profiles, G-Code exporting, and more features for CNC milling.
Importance of Open-Source In Software
Why is open-source CAD software so important?
One of the core appeals is that open-source CAD software allows users, whether that’s an individual or sprawling corporate edifice, to maintain ownership of any drawing, models, files, and any other data created within the program.
Ownership also translates to uncapped and unrestricted commercial use, meaning designs can be used for profit.
Your CAD software-designed IP is yours to keep and use, redistribute, modify, and sell as you see fit. Exporting models or work doesn’t come stamped with an invasive watermark, either.
Furthermore, open-source programs are, by design, developed around compatibility and expandability.
Users can modify, tweak, amend, and customize CAD software’ source code with few restrictions. This aspect is beneficial for users to carve out a bespoke CAD software experience to suit their needs. And if you build your own open source 3D printer kit, such as a Prusa or other RepRap, you have a full open-source workflow for designing and printing parts.
Additionally, open-source means a like-minded community of contributors providing updates and new features to improve the core experience and functionality.
Finally, and probably more importantly for most, open-source CAD software is generally free to use.
At worst, certain advanced features are pay-walled but priced far more affordably than commercial, proprietary CAD programs.
How To Pick The Right Software For You
Performance
Although often free, open-source CAD software must provide all the tools and features for professional applications, matching those bundled into paid CAD programs.
These range from a broad selection of modeling, drafting, and editing tool palettes to file format compatibility and a user-friendly interface.
Rest assured, we’ve only recommended top open-source CAD software widely used by leading companies and professionals with a proven track record.
Active Community and Support
As open-source CAD software relies on users to contribute and improve the underpinning code and expand the feature set, finding a program with a vibrant and active community is crucial.
This ensures the program’s continuous refinement and updates to match industry standards and advances.
Furthermore, the best open-source CAD software communities provide a massive archive of documentation, guides, and troubleshooting help, along with experienced users willing to help troubleshoot and discuss any potential problems or features.
Multitasking
Aside from basic modeling capabilities, the best open-source CAD software weaves in other supplementary features, modes, and functions.
These could be comprehensive 2D sketching tools, simulation modes, design analysis, rendering, automation, and various design techniques such as parametric modeling and boolean operations.
Performing as many tasks within the same program helps workflow and productivity.
Other articles you may be interested in:
- Cura vs Slic3r
- Best 3D animation software
- Best 3D rendering software
- Best 3D sculpting software
- The best CAD software for 3D printing
- Best free 2D CAD software