Key Takeaways
- Concrete 3D printing: A technology that uses specially-formulated concrete and cement mixtures to create 3D objects layer by layer with large-scale printers.
- Types of printers: There are two main types of concrete printers: gantry systems and robotic arm systems. They differ in size, flexibility, and precision.
- Applications of C3DP: Concrete 3D printing has been used for various applications, such as building houses, bridges, wind turbines, coral reefs, and benches.
- Top printers: Some of the top concrete printers on the market are ICON’s Vulcan, COBOD’s BOD2, and CyBe Construction’s RC 3Dp. They have different features and capabilities.
The 3D printed construction industry forecasts a market valuation of $1,575 million by 2024, and a key factor behind this growth is the game-changing technology of concrete 3D printing (C3DP).
The use of 3D printed concrete molds allows for the construction of entire structures within a single day, offering incredible time and cost savings.
So, what’s the science behind this impressive technology?
In this guide I’ll walk you through the leading concrete 3D printing methods, share the top printers available today, and highlight some of the most exciting construction projects!
How Does 3D Concrete Printing Work?
3D concrete printing is similar to regular 3D printing, layering building materials to craft the final product. However, these devices utilize specially-formulated concrete and cement mixtures (not conventional concrete) rather than plastic filament.
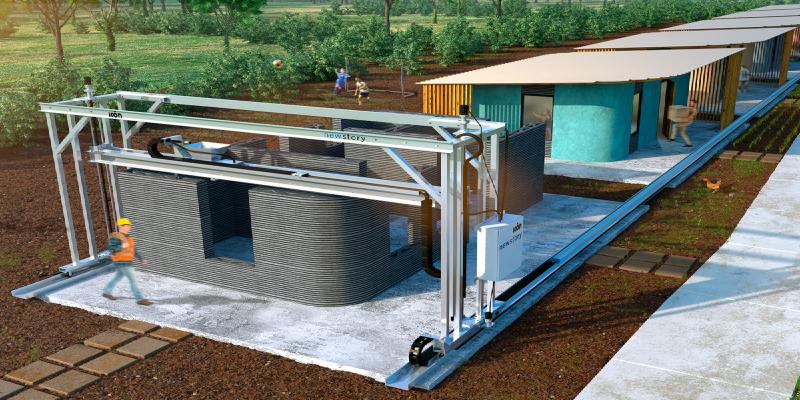

Concrete printers are substantially larger to facilitate the construction of entire buildings or houses. Their software is also considerably more sophisticated, emphasizing geometric precision to ensure the structural integrity of the edifice.
Prior to printing, a 3D model of the intended structure is created using specific software, which is then programmed into the printer. The printer can be established either on-site or off-site, depending on the location of the intended structure, to begin the printing process.
The Different Types of Concrete 3D Printers
There are two main types of concrete printing used in 3D concrete printing: gantry systems and robotic arm systems.
Gantry printer excels in large-scale projects with easier programming, while the robotic arms offers precision and portability (albeit with limitations in scaling up).
Gantry Concrete 3D Printers
The widely used gantry system printers owe their popularity to their large-scale application. Characterized by a hanging print head that operates along the x, y, and z-axes, they function much like the arcade claw game. The printer encloses the target area and constructs the object layer by layer within its range.
The COBOD BOD2 printer, a quintessential example, builds an object by methodically swiveling the print head within its massive frame. Gantry solutions usually cater to larger projects, such as housing and commercial buildings, due to their size.
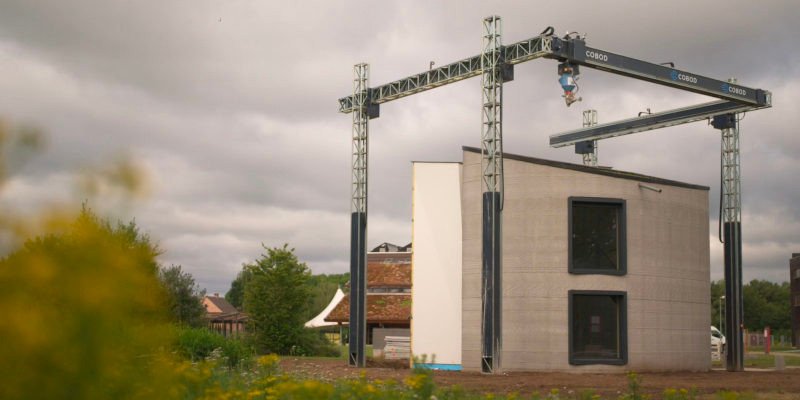

The gantry option stands out for its capacity to offer cost savings for bigger projects. It allows for non-continuous printing without requiring expert programmers. This makes it a fitting choice for large-scale projects prioritizing structure and printing speed.
Robotic Arm Printing
Though not as commonly used as gantry printers, robotic arm concrete 3D printers are just as effective. These printers incorporate a crane-like structure with 6 axes, allowing for greater flexibility and reach than the gantry printers.
The CyBe RC 3Dp. project, a perfect illustration, uses a giant limb-like robot to control and direct the printer head. This allows for precise layering of concrete until the structure is complete.
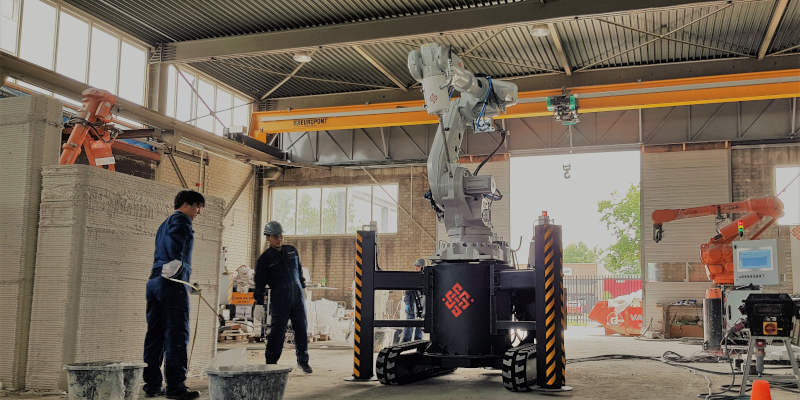

Robotic arm printers exceed gantry printers in terms of detail and compactness. They allow for free-form movements, intricate details, and easier setup and takedown.
Expert engineers are typically needed, but this printer type is adept at handling smaller, more detailed projects due to the precision it affords.
Common Applications for Cement 3D Printing
Cement 3D printing, or C3DP, presents a myriad of possibilities across diverse industries, but its most prevalent use lies in the construction additive manufacturing of 3D printed concrete houses.
The global landscape now features numerous 3D printed houses, a testament to advancements in 3D concrete printing technology. Ongoing projects even envision 3D printing entire communities, heralding a potential shift in housing norms.
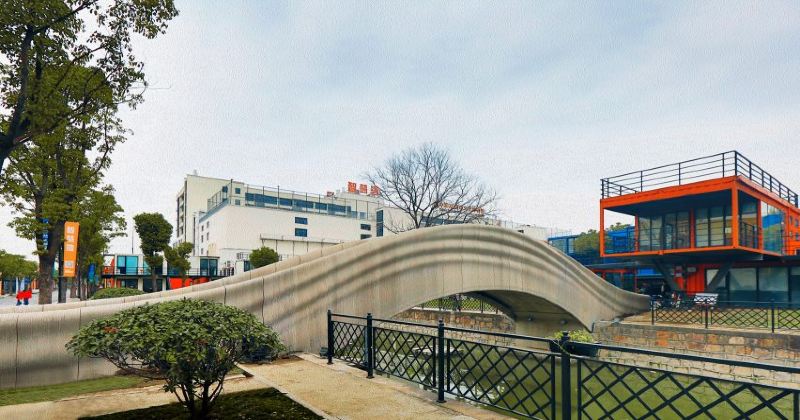

This technology extends beyond residential construction to commercial buildings, as evidenced by offices in Dubai and a hotel in the Philippines.
Moreover, C3DP is not limited to building structures. It’s utilized in constructing bridges, monument letters using MudBots 3D printers, and crafting decorative features such as fireplaces and water fountains. Even civil infrastructure systems like drainage structures are benefiting from this innovative 3D printing technology.
Top 3D Concrete Printing Solutions on the Market
To wind down our trip through the mechanics and uses of concrete printing, we’re going to list the top concrete 3D printers currently on the market and what projects they’ve worked on.
While these printers are the front runners now, this is by no means an exhaustive list of the new technology in additive manufacturing.
ICON’s Vulcan Printer
Starting us off is the gantry-style beast Vulcan, ICON’s 3D printer
The Vulcan is one of the most popular concrete printers on the market, costing up to $250,000, and is known for its extensive use on 3D printing houses across the US and Latin America.
The Vulcan’s specifications boast an 8.5ft print height, 28ft print width, and it precisely extrudes 1in tall, 2in wide cement beads at 5-7 inches per second. Its integrated tech features facilitate controlling the robotics and comprehensive 3D modeling directly from a tablet, with the flexibility to use programmable cement mixtures.
This printer specializes in the efficient construction of ergonomic, single-story homes that are also sturdy and durable.
Current projects you can see the Vulcan in action on is the New Story initiative taking place in Latin America. This project assists economically challenged communities by providing affordable 3D printed homes, fostering new, cost-effective neighborhoods.
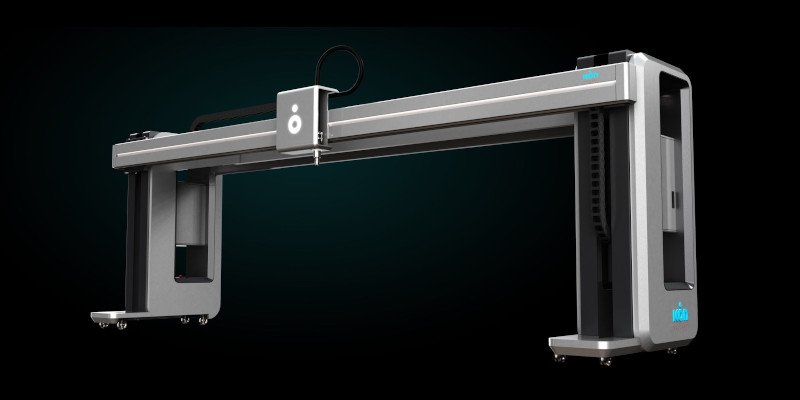

COBOD’s BOD2 Printer
The COBOD BOD2 printer represents a revolutionary advancement in Europe’s 3D construction printing. This second-generation printer boasts a modular design with customizable printer heads enabling comprehensive printing within the walls of its cubic frame.
This advanced printer can fetch up to €1 million and comes in three distinct models, with the largest model presents a printing area measuring 12.10 x 24.75 x 8.14m.
The BOD2’s stands out with its surface mapping tool, allowing it to on irregular terrains by calculating uneven floor patterns. It also accommodates various concrete mixtures with its open material compatibility system.
Its notable contributions include the Kamp C project, the first on-site printed two-story house, and the first 3D printed wind turbine in June 2020. Once logistical issues are addressed, these turbines are anticipated in the field.
CyBe Construction’s CyBe RC 3Dp
Concluding our list is the versatile concrete printer from the Netherlands-based CyBe Construction. They offer two distinct models: a stationary 3D concrete printer for €150,000 and a mobile version for €180,000. Each model includes a robotic arm, proprietary control software, a mix pump system, storage for building materials, and training for up to three users.
The stationary CyBe R 3Dp is ideal for academic research and prototyping, while the more mobile CyBe RC 3Dp excels in construction due to its portability. Equipped with rubber tracks, it smoothly navigates uneven terrain and secures itself with hydraulic feet during the printing process.
CyBe’s portfolio of projects is extensive and diverse. Besides their initiatives in building affordable housing, they have utilized their 3D printing technology in environmental conservation efforts, such as creating artificial coral reefs.
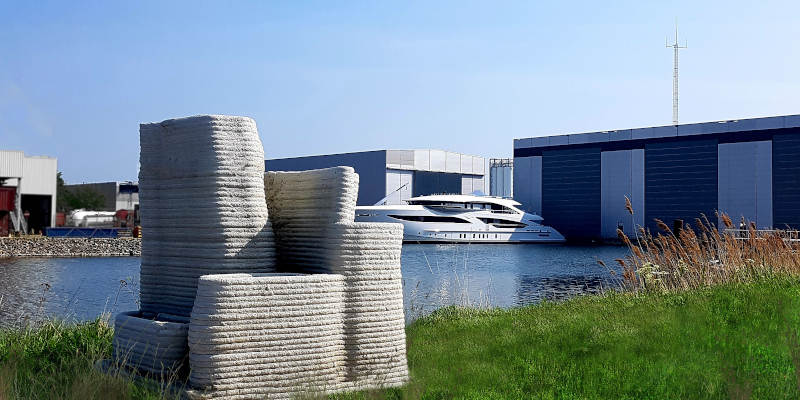

The city of Haarlem in the Netherlands has also commissioned them to furnish the city with a series of 3D printed concrete benches.
These applications emphasize the intricate capabilities of the robotic arm-based printing system and highlight its distinct advantages over gantry-style printers.
Future Outcomes of Concrete 3D Printing
With so many successful outcomes already available, like 3D concrete housing and marine conservation, and more cutting-edge projects underway, it’s hard to believe this technology isn’t affecting more of our everyday lives.
So far, the biggest hurdles in the way of concrete printing are the public’s perception of the safety and potential of this technology, and logistical issues when it comes to size and transport for bigger 3D concrete projects like wind turbines.
That hasn’t stopped people from dreaming big though, as there have been recent discussions about 3D concrete printing in space and developing the first-ever human habitat on another planet.
As we continue to shed light on the possibilities, and companies continue to experiment, we believe it’s safe to assume 3D concrete printing will become widely adopted before long.