Key Takeaways
- 3D printer ghosting and ringing: The article defines ghosting and ringing as 3D printing issues that cause ripples and waves on the surface of the print, especially on corners and edges. It explains the causes and solutions of these issues.
- Causes of ghosting and ringing: The article states that ghosting and ringing are caused by vibrations in the 3D printer, which can result from loose or unstable parts, high print speeds, high acceleration and jerk settings, or models with a lot of direction changes.
- Solutions for ghosting and ringing: The article suggests five easy fixes for ghosting and ringing, such as tightening the 3D printer frame, dampening vibrations, tightening loose belts, slowing down print speeds, and reducing acceleration and jerk settings.
- Resources for more information: The article provides links to other online resources for more information on 3D printer ghosting and ringing, such as guides, tutorials, troubleshooting tips, and case studies.
3D printer ghosting, also known as ringing, echoing, and rippling, is a 3D printing issue caused by vibrations that ruins surface finishes with a rippling effect. These ripples and rings affect print quality, often ruining the print’s overall aesthetic.
It’s called ghosting because the waves left on your surfaces are like the ‘ghosts’ of previous features like corners, as they leave a print defect from corners or embossings on the rest of the surface due to the vibration.
Ringing is especially bad when 3D printing intricate, precise features, like embossed or debossed text. It affects edges and corners, generally making them less sharp, and makes exterior walls look rippled and uneven, affecting flat vertical surfaces.
There are a few reasons for ghosting in 3D printing, and we’re going to look at them here.
What Causes Ghosting or Ringing?
Ghosting is caused by vibration in the 3D printer. If your 3D printer’s frame or build plate is loose or unstable, you don’t have enough vibration dampening from a solid base or rubber feet for your 3D printer, or the wrong slicer settings, this can cause rippling and echoing.
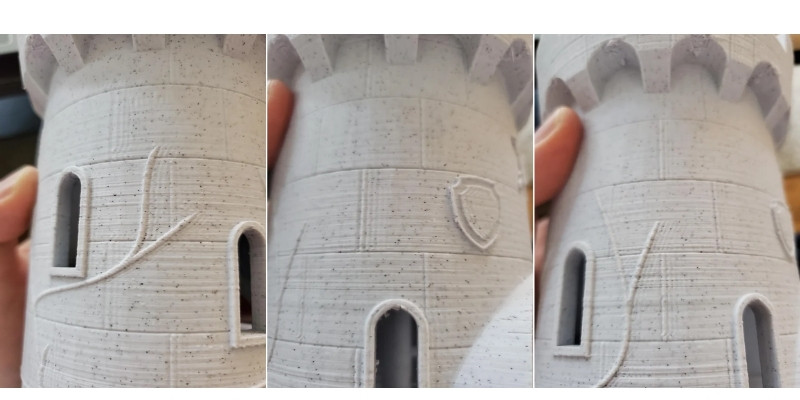
This is because Cartesian FDM printers move along X and Y axes to deposit filament on the print bed, and when they change direction suddenly, like when printing sharp corners and other intricate etails, this sudden movement can reverberate throughout the printhead and extruder.

This is especially pronounced when you have rapid acclerations and decelerations which cause moments of inertia, and resonance. When you change direction, it causes your printer’s frame to flex slightly, creating inaccuracies and ghosting.
Some common causes of ghosting include:
- Loose belts
- Loose screw joints / frame
- A lack of vibration dampening
- High acceleration and jerk settings
- High print speeds
- Too much weight on the print head
- Loose springs
- A model with a lot of direction changes, and sharp edges
How To Fix Ghosting on a 3D Printer (And Prevent it in the Future!)
Here are five simple solutions to 3D printer ghosting, with exactly how you can prevent them from happening again:
- Tighten the loose 3D printer frame
- Dampen vibrations
- Tighten loose belts
- Slow down print speeds
- Reduce acceleration and jerk settings
1. Tighten the Loose 3D Printer Frame
Ghosting, or ringing, often occurs when a part of the 3D printer’s frame is loose, causing vibrations during the 3D printing process.
To fix these ghosting issues, simply tighten the screws and rods that connect your printer together. This ensures the frame is sturdy, and stops it from vibrating too much while printing.
It’s also worth checking to make sure your extruder is fastened tightly, as a loose nozzle can also cause vibrating problems.
More generally, you can prevent 3D printer vibrations by regularly checking over your machine. Every 5 to 10 prints, tighten any bolts and screws to prevent them from getting loose, ensuring smooth 3D prints and preventing ghosting.
Also, check for worn 3D printer parts
Ghosting can also be caused by rods and beams that have become worn, rusted, or otherwise damaged over time, as they will grind together and vibrate your 3D printer.
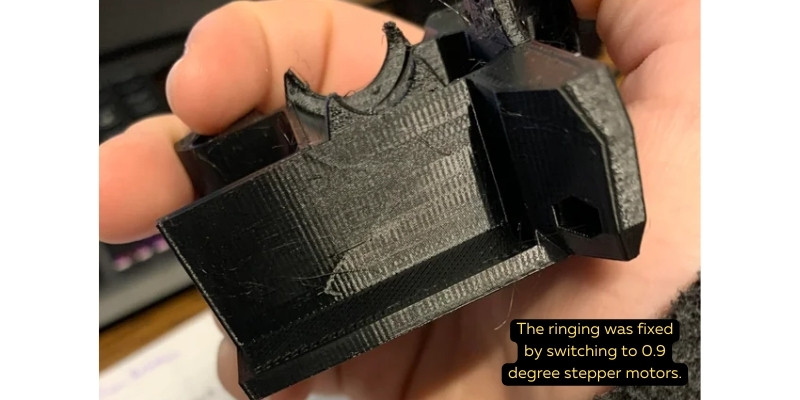
Checking these parts for wear and tear will help you catch 3D printer ringing problems early, and it’s a good idea to replace them whenever necessary. Sometimes, you may just need to wipe these parts down or remove debris that may be caught, which caused them to move against each other with too much friction and vibrate too much.
2. Dampen Vibrations: Solid Base & Vibration-Dampening Feet
Vibrations are common if your 3D printer is on a wobbly or unstable surface, and if your 3D printer doesn’t have any vibration dampening. You need a way to disperse the energy away while 3D printing, otherwise the vibrations will occur in the 3D printer and rattle your frame.
To reduce the chance of ghosting, keep your 3D printer on a good quality table, and use one of several options for dampening vibrations. A solid base keeps the 3D printer secure, and reduces the amount of shaking that can cause echoing in your prints.
Keeping your 3D printer on a sturdy desk is a good start. But for the best results, keep your 3D printer on a thin layer of soft, shock-absorbing material like a rubber mat, which will help keep your printer steady at its base.
Many 3D printers now come with small rubber feet to dampen vibrations, though DIY options like using Styrofoam can work well.
If your 3D printer doesn’t come with these, you can 3D print your own anti-vibration feet, and many of these files exist online. These feet can also help prevent layer skipping.
For example, here are some vibration-dampening feet designed specifically for the Ender 3 that you can download and print from Thingiverse.
3. Tighten Loose Belts
Loose 3D printer belts cause ghosting as a loose belt loses precision with printer movements, leading to the printhead moving around more and causing resonance and vibrations.
This can happen over time as belts stretch or their pulleys loosen, leading to lower belt tension over time. A correctly tensioned belt keeps your printer head
To solve this cause of ghosting, tighten the belts. Some 3D printers have belt tensioners that make this easy, such as the Ender 3 V2, but you can also download and 3D print DIY kits such as this belt tensioner for the Ender 3 Pro.
The belt tensioning procedure varies by which 3D printer you have, but manual belt tensioning usually involves tightening a screw on the pulley. However, be careful not to overtighten during your belt tension adjustment, as excessive belt tension can strain your 3D printer’s motors.
4. Reduce Printing Speed
3D printing too fast causes ghosting problems, leading to higher moments of inertia and rapid changes in direction, causing vibrations and therefore ringing. These vibrations caused by overly fast printing can result in less precise filament placement due to the uncontrolled movements of the printer.
So, lowering your print speed lowers the moments of inertia, and will help reduce vibrations so your extruder can layer the filament more evenly.
To solve this, reducing printing speed lowers moments of inertia and helps mitigate vibrations, as this leads to more controlled layering of filament.
I recommend you reduce your 3D printing speeds in 5mm/s increments until ghosting fades and the surface area of your prints improves. You shouldn’t need to reduce print speeds far below the normal for your filament type.
Even if lowering your print speeds doesn’t fully alleviate ghosting issues, it should still result in better prints overall.
5. Reduce Acceleration and Jerk Settings
Jerk and acceleration settings are two important slicer settings that, if set too high, can cause ringing. This is because when the extruder needs to change direction quickly at higher acceleration speeds, the weight of the print head causes movement and vibrations that prints ripples onto your model’s surface.
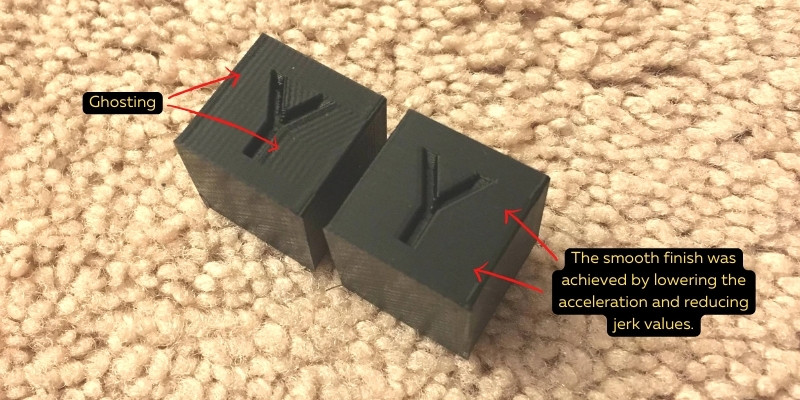
In fact, during The 3D Print General’s tests, he found acceleration and jerk settings to be a more significant factor in ghosting than speed print settings. Though, this experiment was run a few years back.
To solve this, I recommend reducing both your jerk and acceleration settings to lower than the standard settings for your 3D printer. This reduces ghosting and echoing, especially when 3D printing models with many sudden printer movements and direction changes.

In Cura, these settings sometimes need to be enabled first. You can simply search “jerk” and “acceleration” to find them, and they fall into the speed settings in the slicer.
Reducing your jerk setting to around 8-10mm/s, and acceleration print settings to around 1500mm/s², can reduce ghosting and ringing. This is around half the typical acceleration values.
Another lesser-known setting is Outer Wall Acceleration, which when reduced can lessen rippling.
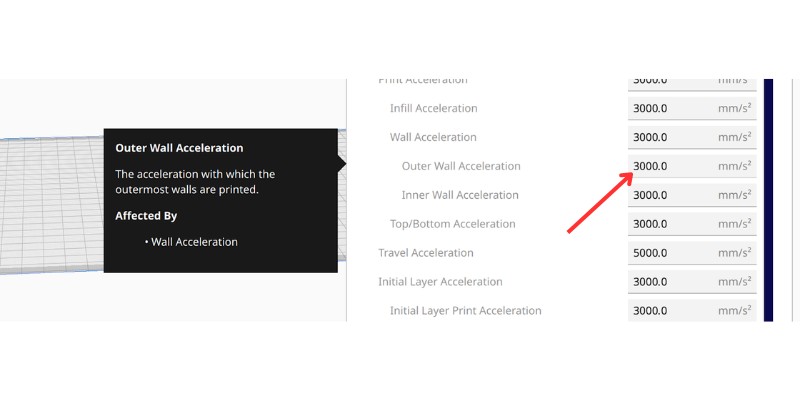
You can also tune your print acceleration to reduce ringing by printing an acceleration tower model. There are many free files you can download online, such as this tower on Printables.
Other Solutions For Ringing
These are less common, but if none of the common fixes above work, consider these:
- Stepper dampeners: these dampen the excess vibrations on your stepper motors, and can also make your 3D printer quieter.
- Optimize 3D models: printing with sharp corners, or with frequent changes in direction, worsens the ghosting effect. Avoiding these changes of movements can improve your model’s final surface finish here.
- Fix loose springs: loose springs that level your bed can cause ringing. Stiffer springs keep the bed steady.
- Reduce weight on your print head – direct drive extruders have heavier print heads than Bowden extruders and more prone to ghosting as a result, as they don’t decelerate as effectively without rattling your 3D printer. In the same vein, if you’re 3D printing with a dual extruder and only using one extruder, then removing the other hot end (and stepper motor) temporarily can reduce ghosting.
Testing For Ghosting – Here Are Some Free STLs
Printing test models to check for ghosting helps prevent it showing up on your favorite projects. Here are some of my favorites:
- Super Simple Ghosting Test by 3DCoded
- Vibration and ghosting test by Orcinus
- Maker’s Muse Ghosting Test
Related posts:
- Gaps and Holes In Your 3D Print? Here’s How To Fix EVERY Cause
- Prevent Blobs and Zits Ruining Your 3D Print’s Aesthetic
- Causes And Fixing 3D Printed Circles Not Coming Out Round?
- What Causes Poor Quality Bridging & HowTo Fix Them